A64 : ADR and ADRP
Content
上周研究OPTEE里关于mmu的部分提到了PIE,OPTEE在启动代码里完成了PIE的实现,这部分代码主要由汇编实现,那为什么这部分代码不受地址位移的影响(link address和load address不一致的情况下)?这就涉及到A64(ARMV8)里PC-rel. addressing的指令了。为了理解什么是PC relative,这篇文章看下ADR和ADRP是如何编码的。
Encoding
PC-rel. addressing指令的编码层级如下:
A64 instruction set encoding
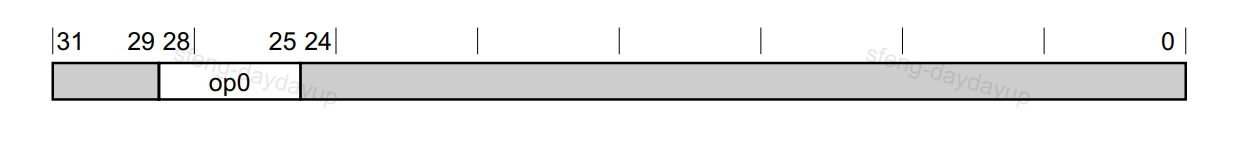
A64先用bit[28:25]把指令分为了以下几个Decode Group:
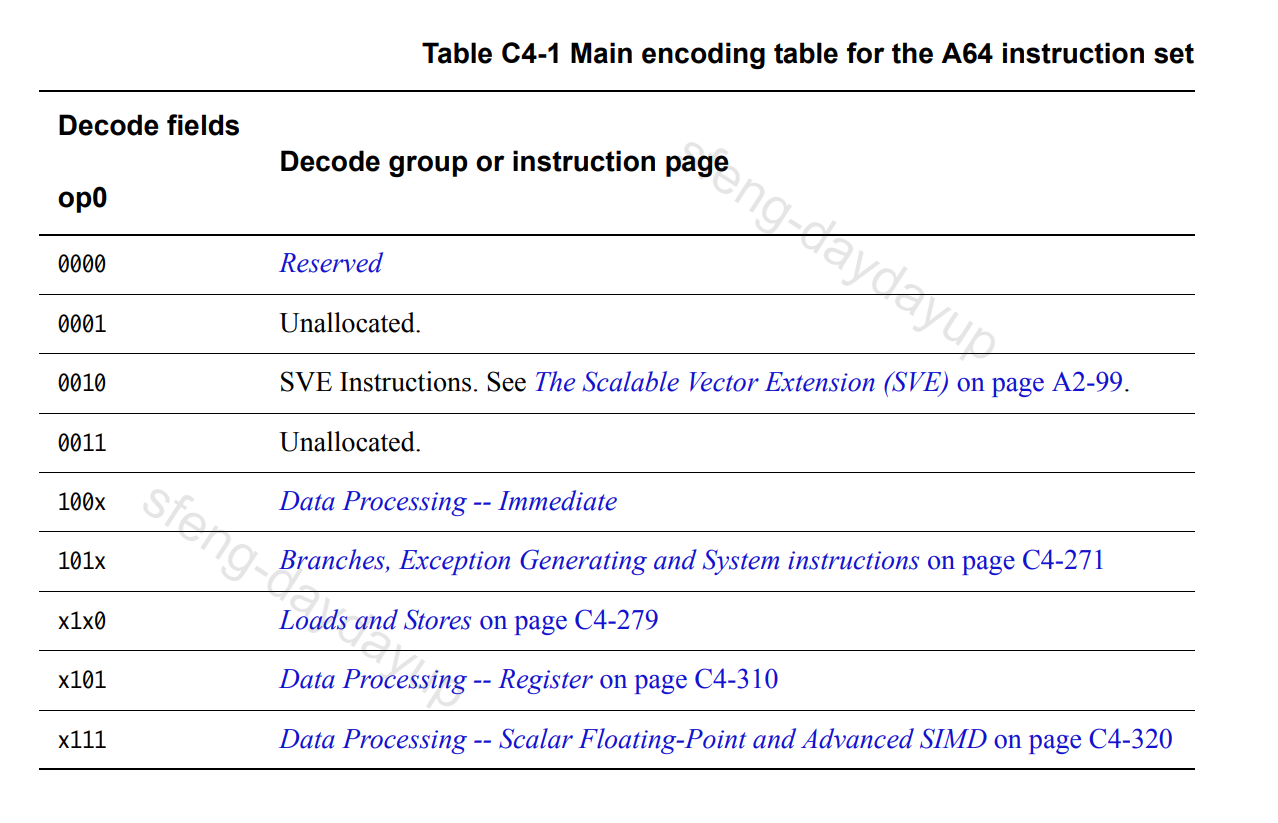
这是第一级的Decode Group,后面在分析其他指令的时候这两张图会经常用。Data Processing – Immediate指令编码
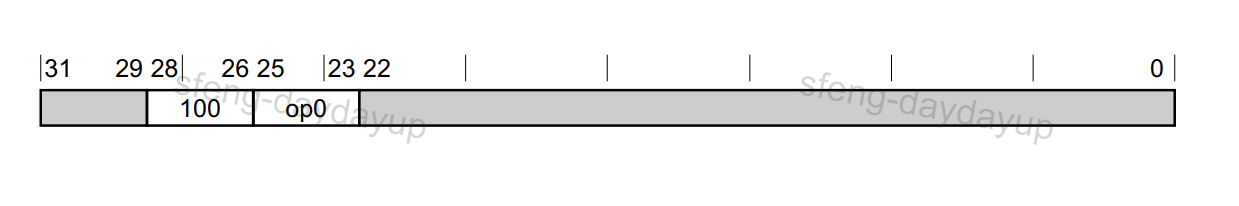
PC-rel. addressing的指令编码属于Data Processing – Immediate的一个Decode Group。
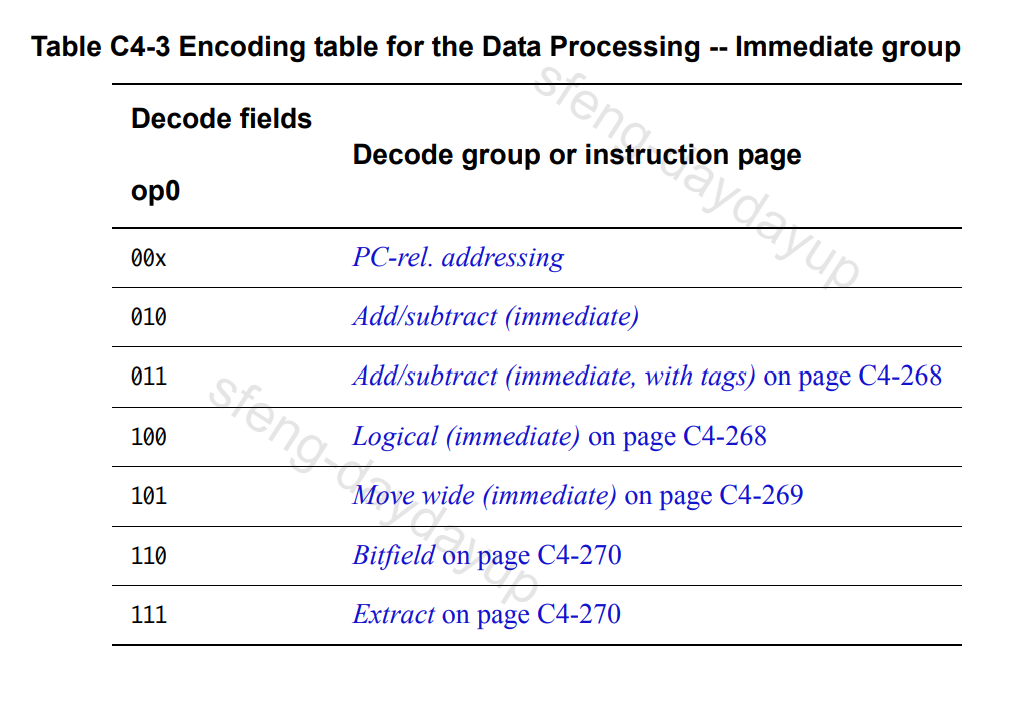
PC-rel. addressing的指令编码
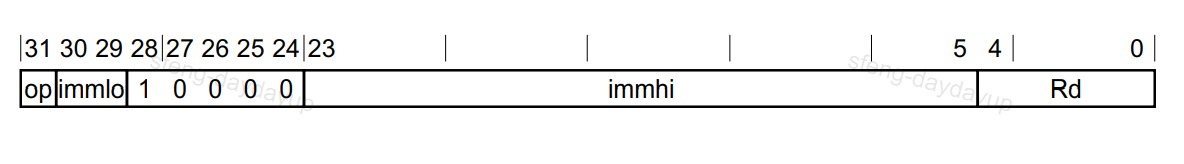
这下到ADR和ADRP了,这两个指令用op(bit 31)来区分,0为ADR,1为ADRP,所以这两个有了不同的行为。
ADR
在上述编码中,bit 31也就是op位为0时,为ADR指令,用法为:
1
2
3
ADR <Xd>, <label>
<Xd> Is the 64-bit name of the general-purpose destination register, encoded in the "Rd" field.
<label> Is the program label whose address is to be calculated. Its offset from the address of this instruction, in the range +/-1MB, is encoded in "immhi:immlo".
在指令编码中,Rd占用5个bit,正好放下X0到X31的index。而immhi和immlo总共21位,最高位为符号位,这也是为什么它的range为+/-1MB。指令执行的结果是把label的实际地址放在Xd里,具体算法为:
1
Xd = PC + SignExtend(immhi:immlo, 64)
这样就Xd里就保存了label目前的真正地址。
ADRP
bit 31也就是op位为1时,为ADR指令,用法与ADR一样,但decode有差别:
1
2
3
ADRP <Xd>, <label>
<Xd> Is the 64-bit name of the general-purpose destination register, encoded in the "Rd" field.
<label> Is the program label whose 4KB page address is to be calculated. Its offset from the page address of this instruction, in the range +/-4GB, is encoded as "immhi:immlo" times 4096.
如上,Rd是一样的描述,而在label的描述里,它的range达到了+/-4GB,为啥呢?因为ADR里的immhi:immlo里就是相对PC偏移地址,而ADRP的immhi:immlo要乘以4KB。这里就有问题了,PC和lable的偏移位置未必就正好是4KB的整数倍啊?别急,先看它是如何计算的:
1
Xd = PC & 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFF000 + SignExtend(immhi:immlo:Zero(12), 64)
竟然把PC的低12位也设为0了,所以这里的immhi:immlo里编码的确实只是4KB对齐的偏移量。得想办法把低12位找回来,来看下OPTEE里如何做得。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
/*
* Load address of <sym> into <reg>, <sym> being in the range
* +/- 4GB of the PC (note that 'adr reg, sym' is limited to +/- 1MB).
*/
.macro adr_l reg, sym
adrp \reg, \sym
add \reg, \reg, :lo12:\sym
.endm
OK,这下清楚了,先把4KB的偏移量赋值给Xd,然后取label的低12位加给Xd。
Example
仍然以OPTEE的代码为例,来帮助理解下。先从objdump里取一个ADR的。
1
2
3
000000000e1001e0 l O .text 0000000000000008 cached_mem_end // link address of cached_mem_end
e100058: 10000c43 adr x3, e1001e0 <cached_mem_end>
adr x3, cached_mem_end汇编编码为0x10007f80。
- bit 31为0,op0为0b10000的话,则为ADR指令
- immlo为0
- op0为0b10000,是PC-rel. addressing指令
- immhi为0b1100010
- Rd为3,目标寄存器为X3
结合immhi和immlo,偏移量为0x188,(0xe1001e0 - 0xe100058)既cached_mem_end的link address减去该条指令的link address也为0x188。因为这条指令和cached_mem_end相对位置不会变,运行到这条指令通过PC+偏移量总能正确找到cached_mem_end。
再来找一个ADRP的。
1
2
3
4
000000000e1d3380 g .nozi 0000000000000000 __end
e107cc4: 90000666 adrp x6, e1d3000 <stack_tmp+0x1d80>
e107cc8: 910e00c6 add x6, x6, #0x380
adr x6, __end汇编编码为0x90000666。
- bit 31为1,op0为0b10000的话,则为ADRP指令
- immlo为0
- op0为0b10000,是PC-rel. addressing指令
- immhi为0b110011
- Rd为6,目标寄存器为X6
结合immhi和immlo,为0xCC,乘以4KB为0xCC000。(0xe1d3000 - 0xe107000)也为0xCC000,同时__end的link address的低12位位0x380,通过第二条add指令还原了低12位,也正确找到了__end的位置。
Perfect!!!
Example in OpenSource
这两个指令是ARM64开发中找到symbol正确的地址和runtime计算link address和load address偏移值的必用指令。大概找了下开源项目中boot code中使用这两个指令的地方。如下:
- ATF https://github.com/TrustedFirmware-A/trusted-firmware-a/blob/v2.9/lib/aarch64/misc_helpers.S#L518
- OPTEE https://github.com/OP-TEE/optee_os/blob/4.0.0/core/arch/arm/kernel/entry_a64.S#L282
- uboot https://github.com/u-boot/u-boot/blob/master/arch/arm/cpu/armv8/start.S#L84
- Linux https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v5.15/arch/arm64/kernel/head.S#L94
理解这两个指令的编码方式对阅读理解或者开发boot code有很大帮助。
Reference
DDI0487Fc_armv8_arm.pdf