Hodgepodge of ARM
Preface
这篇来个ARM的大杂烩吧,主要是把收集到的一些和ARM相关的知识和信息做个汇总,以备查阅。发现Arm官网真是个宝藏,内容多的很可能穷尽职业生涯也学不完,只取所需吧。
Content
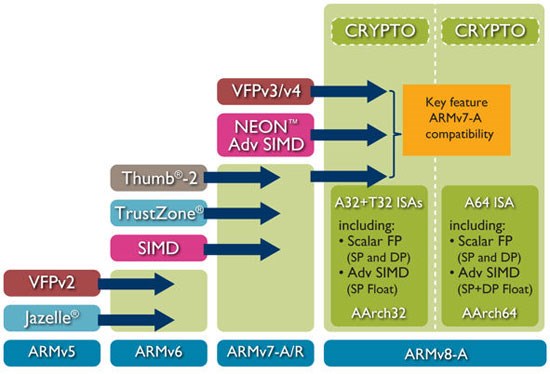
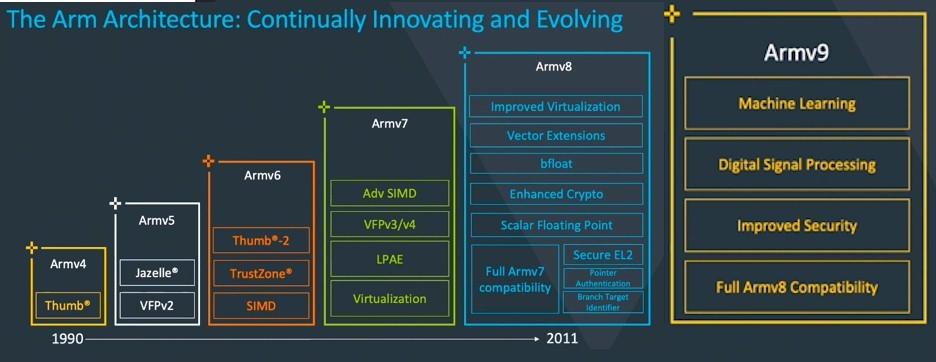
Path of ARM Evolution
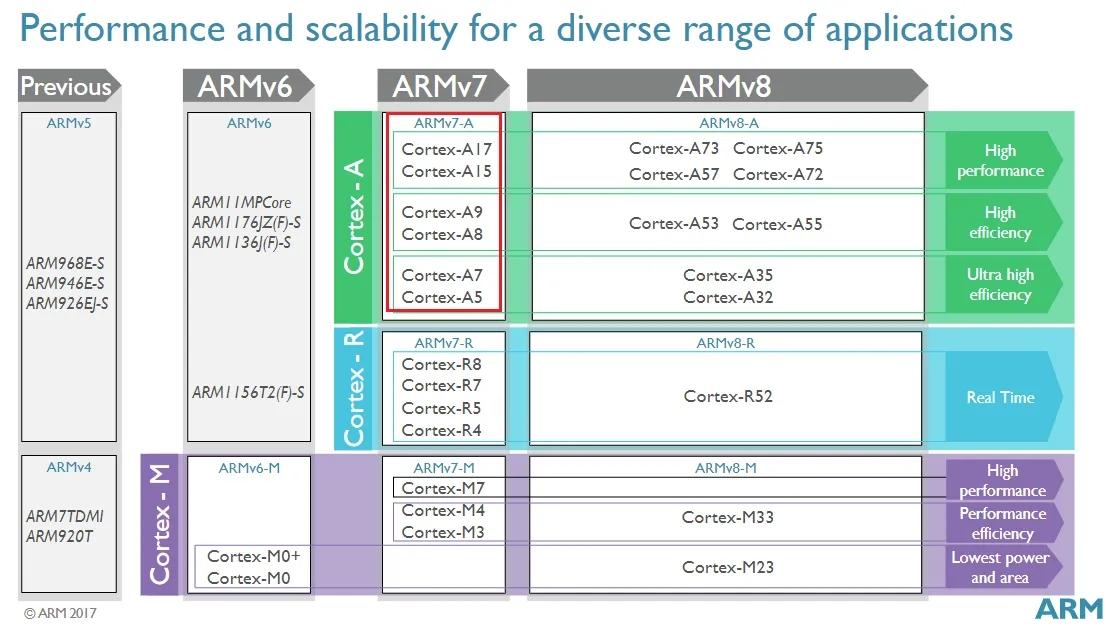
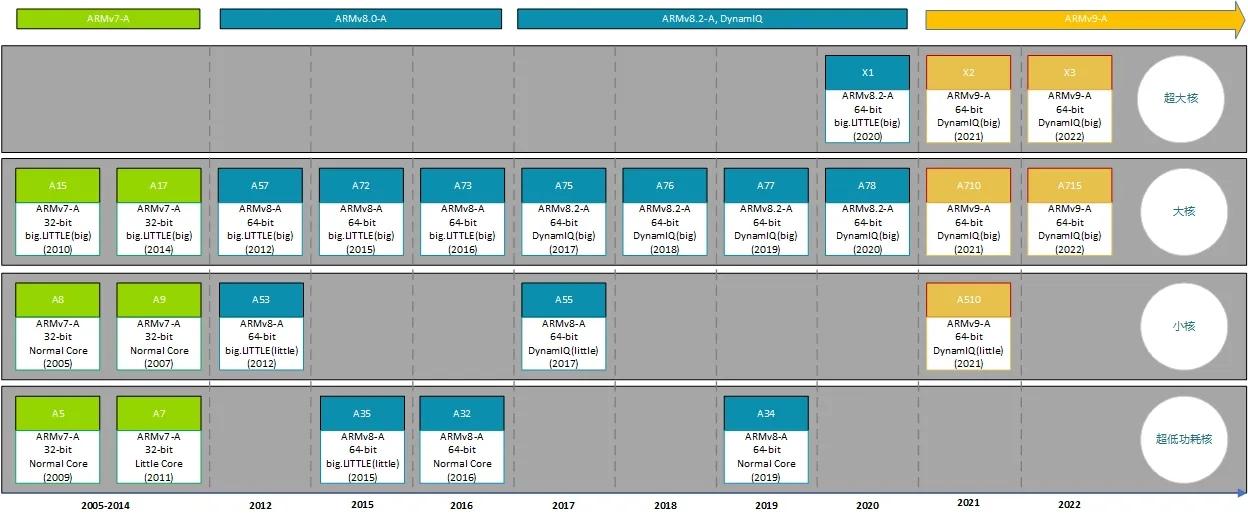
从ARMv8开始,ARM更新太快了,一年一更(见Reference里引用blog里的 announcement),以至于上面这张图显得太简略了。在网上又搜了几张图,其实也不算最新,索性一并放上来。
从上面的图片可以看出从ARMv7开始形成了Cortex-A、Cortex-R和Cortex-M系列的路线图。相比于R和M系列,A系列则更是紧跟ARM发展的脚步,每一代的新技术都会有代表芯片出炉。
ARM Family
除了常用的A、R、M系列(咦,恰巧是ARM,然而它是Advanced RISC Machines的缩写),还有X和Neoverse系列等等。X系列其实还是A系列的衍生,N主要用于服务器端,我们做embeded system的目前没接触过,总体还是以A、R、M三个系列为主。
Cortex-A Series: These processors are designed for high-performance applications, such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops. They are known for their powerful processing capabilities and are often used in conjunction with GPUs for graphics-intensive tasks.
Cortex-R Series: This series is tailored for real-time applications, such as automotive systems and industrial control. They offer a balance between performance and predictability, critical in safety-critical systems.
Cortex-M Series: Designed for microcontroller and embedded applications, these processors are known for their energy efficiency and determinism. They are widely used in IoT devices, wearables, and other battery-powered gadgets.
Cortex-X Series: Performance-First Design. Close collaboration with Arm enables program partners to influence products and achieve tangible improvements for market-specific use cases. Compatible with Arm Cortex-A CPUs for design flexibility and scalability with DynamIQ support for intelligent solutions.
Neoverse: ARM’s server-grade processors are part of the Neoverse family. They are designed to meet the demands of data centers and cloud computing, offering scalability and power efficiency.
博主用过的ARM的芯片其实也很有限,A系列里最老的用过ARMv5te架构的CPU,后来就是V7架构的Cortex-A7、Cortex-A15,再后来尝鲜了V8架构的Cortex-A53,后边就基本都是V8架构了,诸如Cortex-A55、Cortex-A72、Cortex-A73,还有ARM给车规级芯片准备的Cortex-A78AE。R系列里也是做车规芯片的时候用过Cortex-R52。M系列比较简单,Cortex-M3和Cortex-M33,一般跑个RTOS加一些task上去。
Brief of Some Features
今天算是重新学习ARM架构了,这里列一些个人认为比较有用或者有趣的feature。
Thumb-2
根据官方文档描述,Thumb-2混合了32位指令和16位指令,可以提供和A32一样的性能的同时还可以保持不错的code density(30% improvement)。所以运行在aarch32时,建议编译为Thumb-2。
TrustZone
TrustZone是ARM推出的一种系统级的安全解决方案(ARMv7开始)。它不单纯是一个硬件方案,也包含软件实现。SecureMonitor,OPTEE,Trusty等等都是基于TrustZone的一种软件实现。
SIMD,Neon,SVE,SVE2
单指令多数据流,并行加快数据处理和提高性能。矩阵乘法、高性能计算、机器学习。
Virtualization
从ARMv7开始支持虚拟化,在ARMv8又有加强。通过跑在EL2的hypervisor(REE world),可以同时有几个VM跑在硬件平台上,且互不干扰(至少表面看来是)。Hypervisor还分type1和type2。比如QNX和Xen就是type1,KVM是type2。
SecureEL2
增加了secure world的虚拟化支持。通过在Secure EL2的SPM,TEE端也可以同时跑几个TrustZone kernel了。这个feature从ARMv8.4开始。
Pointer authentication
这是ARMv8.3新增的feature,这个貌似是解决stack overflow和buffer overflow更高效的方案,等仔细研究过后在更新。
Cryptographic Extension
ARMv8开始的Cryptographic Extension支持AES、SHA1和SHA256,随后在ARMv8.2(spec上为8.2,但arm blog上的announcement里则表示8.4才开始)里增加了SHA512、SHA3、国密SM3和国密SM4的支持。之前在Cortex-A78AE上测过AES各种模式和SHA256的性能,性能很可观,有空在树莓派上再测一下。
Memory Tagging(MTE)
这貌似也可以作为防止堆和栈溢出的解决方案啊,“Deploying MTE in Software”这节里也讲了Heap tagging和Stack tagging。肤浅了,真是书中自有颜如玉啊,书中真有解决方案。不过这个feature要在ARMv8.5才能用了。
Branch Target Indicators(BTI)
In Armv8.3-A, we introduced the Pointer Authentication feature, which can be used to ensure functions return to the location expected by the program.
In Armv8.5-A, we introduce Branch Target Indicators (BTI). Systems supporting BTI can enforce that indirect branches only go to code locations where the instruction is one of a small acceptable list. This reduces the ability of an attacker to execute arbitrary code.
These two features work together to significantly reduce the number of gadgets available to an attacker. The gadgets that remain available are large in size, making it much harder for an attacker to make a viable exploit, even if they find a vulnerability that lets them gain access to a machine.
原来ARM一直在解决这个问题啊。
Atomic 64-byte load and stores
64字节数据读取和存储的原子操作只能从ARMv8.7开始支持了。
WFE and WFI with timeouts
这个功能貌似有可以利用的地方。不过也是ARMv8.7以后的事了。
Optimizing for the memcpy() family of functions
这个属于闷声发大财,不自己写string库的话,对用户是透明的。ARMv8.8才有的feature了。
Guarded Control Stack (GCS)
GCS provides mitigations against some forms of ROP attacks. GCS also provides an efficient mechanism for profiling tools to get a copy of the current call stack, without needing to unwind the main stack. 又是一个防止ROP和JOP的。懒的翻了。ARMv8.9-A和ARMv9.4-A。
Confidential Computing(CCA)
这个是ARMv8.9-A和ARMv9.4-A引入的新东西了。把secure和non-secure又细分为root、realm、secure和non-secure了。具体看reference里的CCA。
Live migration
这个比较有趣,可以把一个VM从当前host migrate到另外一个host。ARMv9.5-A。
Checked Pointer Arithmetic
Taking the previous MTE example, the new features allow the processor to detect if the top 8 bits of the pointer have been modified. This means that if the MTE tag were corrupted it would be reported back to software.继续Copy,对内存特别是指针的保护是不遗余力啊。ARMv9.5-A。
Summary
哈哈,总结一下:
- ARM官网确实是个宝藏。
- 解决之道就在书中。
Reference
Arm Architectures and Processors blog
Arm-M Profile Arch
Arm-R Profile Arch
ARMv8.1 overview
Armv8.2 overview
Armv8.3-A overview
Armv8.4-A Introduction
Armv8.5-A
Armv8.6-A
Armv8.7-A
Armv8.8-A and Armv9.3-A
Armv8.9-A and Armv9.4-A
Armv9.5-A
ARM Memory Tagging(MTE)
CCA(RME)