SA and SAU
Preface
SA和SAU是由Armv8-M的security extension引入的。是Cortex-M系列中实现TZ的重要组成部分。本文对它们做个初步介绍。
SA
关于SA,简单点讲就是把memory分成了下面几种type:
- Non-secure 在Arm Cortex-A系列里,non-secure的resource是其他所有状态下都可以访问的。然而在Coretex-M里并不是,在设计的时候一般都会给物理内存两段映射地址,一段供secure state访问,如[0x10000000 - 0x10040000],一段给non-secure state访问,如[0x00000000 - 0x00040000]。在SAU设置某段物理内存为non-secure就是设置non-secure的地址区间,如[0x00003000 - 0x00004000],这段地址secure state是不能访问的,但可以通过secure的地址映射[0x10003000 - 0x10004000]来访问。
- Secure and Non-secure callable 只有secure processor可以访问,允许non-secure world在这个区域内调用函数,当然要通过SG指令。
- Secure and not Non-secure callable 只有secure processor可以访问。
另外还有exception。
0xF0000000 - 0xFFFFFFFF
If the PE implements the Security Extension, this memory range is always marked as Secure and not Non-secure callable for instruction fetches.
If the Security Extension is not present, this range is marked as Non-secure.
以及下面的地址由当前processor的security state决定。
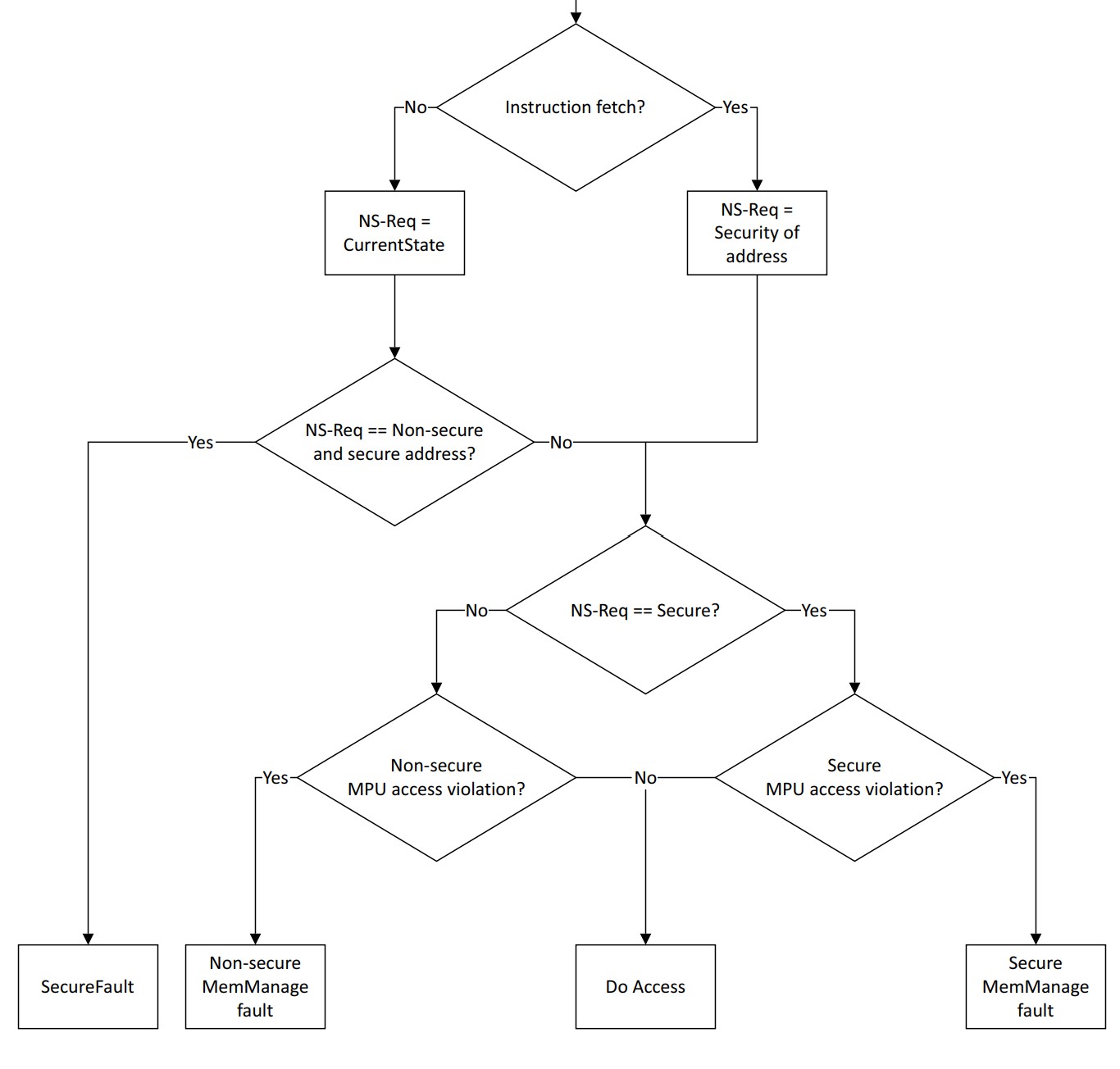
The following address ranges are marked with the Security state indicated by NS-Req, that is, the current state of the PE for non-debug accesses. This marking sets the NS-Attr to NS-Req:
0xE0000000 - 0xE0002FFF: ITM, DWT, FPB.
0xE000E000 - 0xE000EFFF: SCS range.
0xE002E000 - 0xE002EFFF: SCS NS alias range.
0xE0040000 - 0xE0041FFF: TPIU, ETM.
0xE00FF000 - 0xE00FFFFF: ROM table.
0xE0000000 - 0xEFFFFFFF for instruction fetch only.
Additional address ranges specified by the IDAU.
Note: NS-Req defines the Security state that the PE or DAP requests that a memory access is performed in. 对应关系如下:

下图是“Security attribution and MPU check sequence”。
SAU
S先列下几个关于SAU的rule:
- RMPJC Memory is marked as Secure by default. However, if the address matches a region with SAU_REGIONn.ENABLE set to 1 and SAU_REGIONn_NSC set to 0, then memory is marked as Non-secure。
- RWGDK An address that matches multiple SAU regions is marked as Secure and not Not-secure callable regardless of the attributes specified by the regions that matched the address。
SAU Registers
SAU的寄存器有点类似MPU的,当然功能是不一样的。
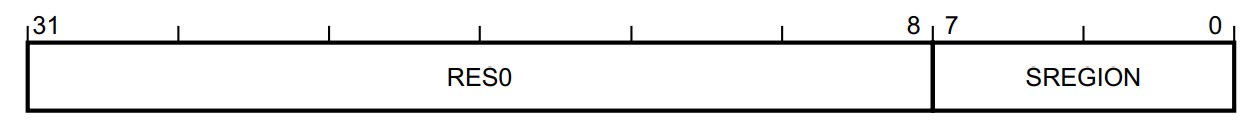
SAU_TYPE
- SREGION, bits [7:0] 读取该寄存器获取可设置的SAU region的数目。如果是0,则SAU一切都没有了意义。
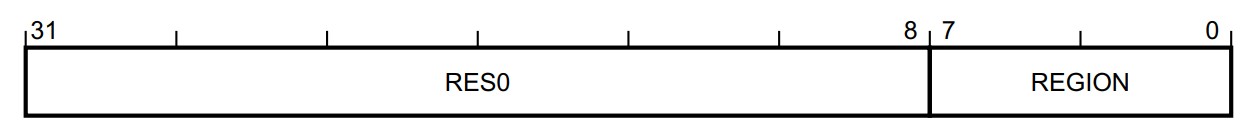
SAU_RNR
- REGION, bits [7:0] 选定要配置的region的index。范围是从0到SREGION - 1。
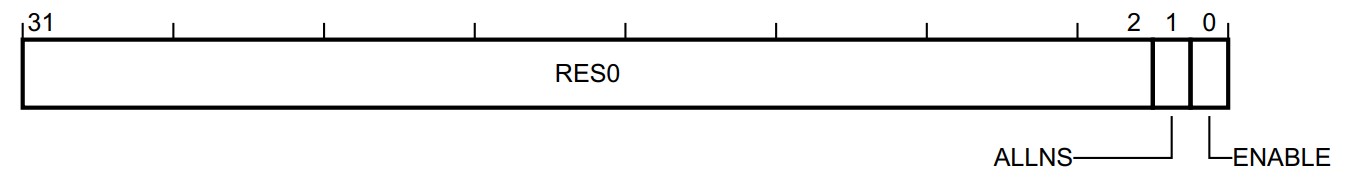
SAU_CTRL
- ALLNS, bit [1]
- 0 Memory is marked as Secure and is not Non-secure callable
- 1 Memory is marked as Non-secure
- ENABLE, bit [0] 是否enable SAU
这里需要说明的是,如果disable SAU,并且系统中也没有IDAU,那么reset回来系统默认的Secure state是无法改变的,也就是无法切换到non-secure state下。
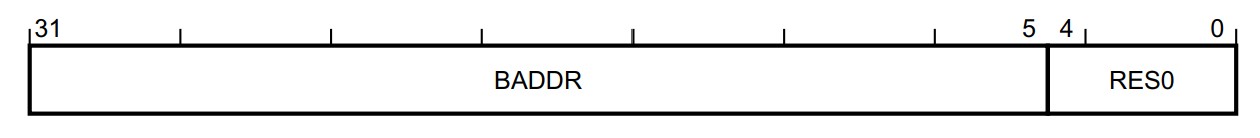
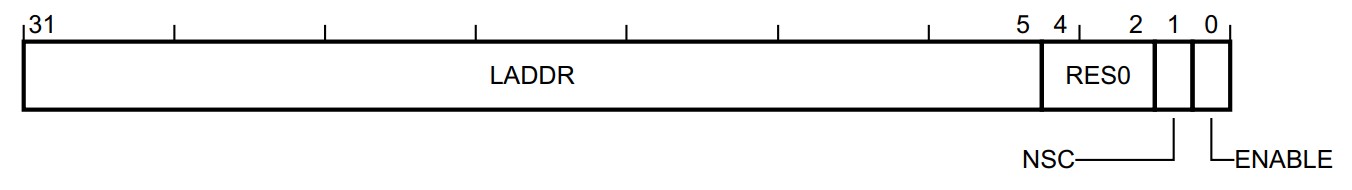
SAU_RBAR
- BADDR, bits [31:5] 设置RNR寄存器选定region的及地址,同MPU一样,32B对齐。
SAU_RLAR
- LADDR, bits [31:5] 设置当前选定region的范围。32B对齐。
- NSC, bit [1]
- 0 Region is not Non-secure callable 这里貌似不够明显,查看了一些资料和代码,设为0则该region是non-secure。
- 1 Region is Non-secure callable (secure,non-secure callable)
- ENABLE, bit [0]
- 0 SAU region is disabled
- 1 SAU region is enabled
另外还有两个寄存器SFSR和SFAR用来出错时debug用。
- SFSR Provides information about any security related faults
- SFAR Shows the address of the memory location that caused a Security violation
Application
系统启动后一般SAU默认是disable的,这样在切换到non-secure的时候要做相应设置。如前所述,一定要设为enable才能切换到non-secure。另外为了安全性,应该默认所有的memory为secure。这样SAU_CTRL的设置为:
1
2
SAU_CTRL.ALLNS = 0;
SAU_CTRL.ENABLE = 1;
为了让non-secure OS能够运行,要通过SAU设置至少一块non-secure的memory。例如:
1
2
3
4
5
SAU_RNR.REGION = 0;
SAU_RBAR.BADDR = 0x200000;
SAU_RLAR.LADDR = 0x400000;
SAU_RLAR.NSC = 0;
SAU_RLAR.ENABLE = 1;
当然还要设一个secure,callable的region供non-secure world调用secure world提供的API。
1
2
3
4
5
SAU_RNR.REGION = 1;
SAU_RBAR.BADDR = 0x400000;
SAU_RLAR.LADDR = 0x500000;
SAU_RLAR.NSC = 1;
SAU_RLAR.ENABLE = 1;
最后,关于IDAU由于是implementation defined,遇到具体实例再补充。
Reference
Armv8-M Architecture Reference Manual
TrustZone technology for the ARMv8-M architecture Version 2.0
Memory system and memory partitioning